In this tutorial, I will share how control a unipolar stepper motor
using STM32F103 microcontroller. If you don't know the basic of the
stepper motor, I suggest you to read this article first. To control a
stepper motor from microcontroller, we can't directly drive it with GPIO
pins because GPIO pins have maximum current that can sink or source
from it. To overcome this problem, we can use driver circuit. The driver
circuit for unipolar stepper motor can be built by using 4 transistors
to drive large current every 4 wires of a stepper motor. It also can be
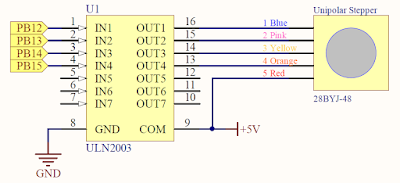
built with ULN2003 IC. This is the circuit for driving a unipolar
stepper motor from microcontroller by using ULN2003 IC:
In this tutorial, I will use 28BYJ-48 stepper motor. This motor is very cheap and it also comes with driver module based on ULN2003 IC. This motor runs with 5V supply and has gear inside. The gear reduction ratio is approximately 64:1. If you search from internet, other people say that the gear reduction ratio is actually 63.68395:1.